WHITEPAPERS
The Ultimate Guide to IoT Connectivity
IoT connectivity refers to the technologies, protocols, and networks that allow IoT devices to connect and communicate with each other and the internet.
Imagine living in a high-rise apartment building that can predict (and prevent) imminent HVAC failures. Or picture stepping into a healthcare facility where devices gather biometric data to optimize patient care in real time. These scenes aren’t something out of a science fiction novel: this is the real, transformative power Internet of Things (IoT) devices have on our world.
From smart homes to healthcare, manufacturing to transportation, IoT devices are revolutionizing industries and improving lives. It should come as no surprise, then, that the corporate appetite for IoT is expanding rapidly — 94% of companies globally are actively exploring or implementing IoT, signaling its widespread status as a strategic business asset. But enthusiasm alone won’t guarantee success in IoT adoption. Smooth deployment hinges on several factors, including IoT connectivity. It’s crucial for harnessing the full potential of connected devices, enabling data-driven decision-making, improving efficiency, and driving innovation. This article will cover everything you need to know about IoT connectivity and, for those who’d like to learn more, provide some in-depth technical resources along the way. Let’s dive in.
At the heart of this revolutionary technology lies robust and reliable connectivity — the backbone that brings the Internet of Things (IoT) to life.
IoT In Action: A Brief Snapshot Of IoT Devices
All kinds of IoT devices exist on the market. They have several functions, including sensing, monitoring, remote control, and actuation. The smart thermostat in that potential highrise, for example, would likely include an integrated circuit to sense temperature, as well as a relay to actuate the HVAC system and prevent catastrophic failure. But to provide a clear-cut example of how IoT devices work, we’ll describe them here in the context of an advanced manufacturing facility.
Manufacturing facilities generally consist of assembly lines that combine both human and machine-powered activity. These machines are equipped with sensors to communicate with each other, making real-time decisions about factors including quality control, maintenance needs, and inventory.
In this setup, an anomaly detected by one machine can trigger an alert or an immediate response from another, ensuring the assembly line’s smooth operation. These devices, which are physical pieces of hardware programmed to interact with people, systems, and other devices across the internet, are the “things” communicating with each other in the system — the “T” in “IoT.”
The Very team was able to see this functionality in action at a recent visit to a manufacturing partner. The facility used a robotic arm to pick up a circuit board and automatically shuttle it between multiple assembly and inspection steps. If any of those inspection sensors determined anomalies in the board, the arm would set the board aside for scrap or rework.
IoT devices find applications in consumer, enterprise, and industrial environments, providing real-world functionality and creating a network of connected devices.
If you’re considering building or utilizing one, get familiar with these fundamentals first.
IoT Connectivity: The Backbone of Successful IoT Deployment
When we talk about IoT connectivity, we’re referring to the behind-the-scenes infrastructure that allows IoT devices to connect and communicate with each other and the internet. Connectivity encompasses the technologies, protocols, and networks that facilitate the exchange of information between IoT devices, enabling them to operate intelligently and deliver value in various applications.
In simple terms, IoT connectivity allows devices to connect to the internet, other devices, or a central hub to transmit and receive data. It enables monitoring, control, and data analysis, paving the way for automation, optimization, and innovation across industries.
What To Know About IoT Connectivity
IoT connectivity is typically associated with the transfer of data, but it encompasses much more than that. Connectivity is a crucial component to the success of an IoT product, underpinning the functionality and value of IoT solutions regardless of their application. By prioritizing a robust connectivity infrastructure, companies open the door to enhanced automation, greater predictability, and increased efficiency.
Imagine a large grocery store chain with IoT-enabled refrigerators. These devices consistently relay temperature and humidity data to a central system to prevent food from spoiling. Without reliable IoT connectivity, that data flow is interrupted, potentially leading to significant losses, food waste, and increased health risks for consumers.
Like big grocery chains, countless operations depend on consistent IoT connectivity to maintain optimal safety, profitability, and seamless operational functioning.
It’s worth noting that significant strides in IoT can be made even with networks that don’t offer real-time communication. Reducing communication rates below real-time can enable to use of low-power, long-range assets that are critical to industries like infrastructure and utilities. This enables digital transformations in industries that aren’t traditionally considered “IoT-friendly.”
How IoT Connectivity Works
At its core, all IoT connectivity consists of three base ingredients: the protocol, the network architecture, and the cloud services. All three components must be designed to work together frictionlessly to facilitate smooth data exchange and communication.
- Protocols are the languages IoT devices use to communicate both with each other and with the broader network. They range from household names (WiFi, Bluetooth) to more niche IoT-specific protocols (LoRaWAN, NB-IOT). Some IoT networks include a mix of protocols to address different needs. It’s important to understand the intended use case and advantages/limitations of your chosen protocol to apply it effectively in an IoT network.
- Network architecture is the next important piece of the IoT connectivity puzzle. There are four primary types of IoT networks: Cellular, Local Area Network (LAN), Low-Power Wide-Area Network (LPWAN,) and Mesh. Each configuration involves different implications for cost, range, power use, and data throughput. Consider these with your intended use before deciding on a network architecture for your IoT product.
- The cloud service is your IoT data’s final destination. Cloud services provide the infrastructure for storing, processing, analyzing, and displaying the massive amounts of data generated by IoT devices. Cloud-based IoT platforms also enable reliable and efficient management of IoT devices, including device updates, remote monitoring, and control.
If you’re interested in the functional intricacies of IoT connectivity, you can take a deeper dive into this resource here.
Communication Protocols
Choosing the best IoT protocol for your specific needs depends on various factors, including the nature of your IoT application, data requirements, network infrastructure, scalability, security considerations, and compatibility with existing systems. These protocols can be designed for wired or wireless communication. Here are some common protocols we use at Very during IoT production design:
- LoRaWAN: A relative newcomer on the scene, LoRaWAN (Longe-Range Wide Area Network) has undergone a generous uptick in adoption over the past few years. Boasting the potential for long-range (up to 15 km!) at low power consumption, LoRaWAN is an attractive choice for long-range networks with low data throughput. However, LoRaWAN devices cannot talk directly to the cloud and require a gateway to relay data.
- LTE-M: This protocol allows individual devices to connect directly to the cloud. LTE-M (Long Term Evolution – Machines) is part of the 4G cellular network specifically targeted at IoT devices. LTE-M is designed to be a “battery-friendly” cellular protocol, allowing the device to enter a low-power mode between transmissions.
- WiFi: WiFi is a common, tried-and-true wireless communication protocol. It’s robust and possesses several operational modes and frequencies. WiFi devices connect to the cloud through a router, so they can’t stand alone like cellular devices can.
- Bluetooth: Bluetooth, another common communication protocol, allows short-range device-to-device connectivity. Bluetooth’s major strength lies in its flexibility and ease of onboarding. New Bluetooth devices can be set up in seconds and configured as Mesh devices, significantly increasing their effective range.
- RS-232: First developed in 1960, RS-232 is probably best remembered today for connecting printers to computers back in the 80s and 90s. Even considering its age, RS-232 has an important part to play in the IoT ecosystem. Including older, wired protocols on IoT devices allows them to interface with older commercial and industrial equipment. In certain industries, where equipment can be used for 50+ years, RS-232 can enable digital transformation without requiring a whole new factory worth of tools.
Types of IoT Networks
The type of network your IoT device uses can have big implications for your business. Different types of networks have different data rates, cost models, and provider support. Below are some of the most common IoT network types:
- Cellular: Cellular IoT networks leverage the significant cellular infrastructure that telecom companies maintain globally. Devices connect directly to these networks and transmit data to the cloud, meaning you don’t have to manage any additional infrastructure. Typically, companies pay per megabyte of data sent, meaning large networks could generate correspondingly large cellular builds. Even so, cellular is an extremely attractive option for IoT devices that are deployed into areas without other support infrastructure.
- LAN: Local Area Networks (LAN) are locally managed connections to the cloud. Data from multiple devices is fed to the cloud through a single device (known as a router). LANs are typically found in residential homes — routers are connected to a wired internet connection (such as cable and fiber), and then all devices connect to that router via WiFi or Cellular. LANs are usually quite limited in the protocols they work with; WiFi and Ethernet are the most common.
- LPWAN: Low-Power Wide Area (LPWAN) networks utilize protocols that prioritize extending range and minimizing power use over all else. They typically rely on niche protocols that require a gateway to connect to the internet. Essentially, the individual IoT devices talk directly to the gateway over the LPWAN network, while the gateway collects that data and sends it to the cloud using a more traditional protocol (such as WiFi or Cellular). If you’re looking to deploy a large number of battery-powered IoT devices over a wide area, LPWAN may be the right choice.
- Mesh: Like LPWAN networks, Mesh networks utilize the gateway to collect data and send it to the cloud. The primary difference between Mesh and LPWAN is that individual Mesh devices can talk to each other, as well as to the gateway, enabling users to use shorter distance protocols (like Bluetooth) and “leapfrog” data between devices to extend the effective range. Mesh networks can be extremely robust and well-suited for scaling.
Challenges of IoT Connectivity
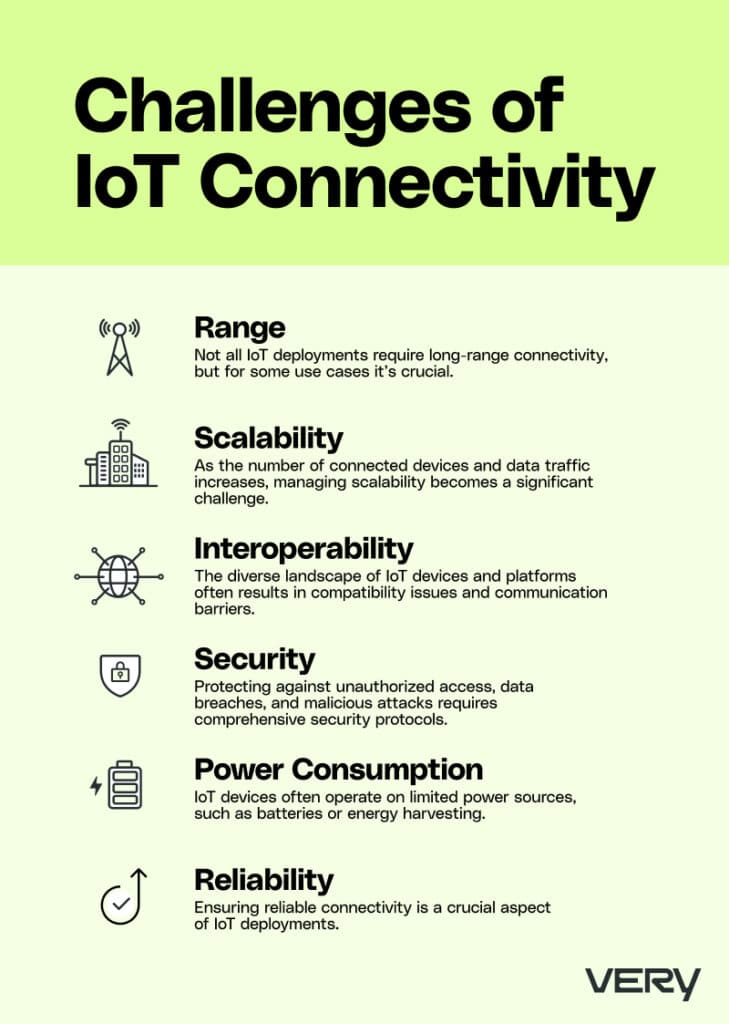
Like all technologies, IoT connectivity isn’t without its challenges. Here are a few common hurdles to be aware of as you deploy and scale your IoT devices:
- Range: Not all IoT deployments require long-range connectivity, but for some use cases it’s crucial. The ability to transmit and receive data effectively across vast areas presents unique challenges in terms of signal strength, coverage, and network infrastructure.
- Scalability: As the number of connected devices and data traffic increases, scalability becomes more complex. IoT ecosystems must accommodate the growing influx of devices, handle data efficiently, and maintain seamless connectivity without compromising performance.
- Interoperability: The diverse landscape of IoT devices and platforms often results in compatibility issues and communication barriers. Ensuring interoperability between different devices and systems is vital for smooth deployments.
- Security: Protecting against unauthorized access, data breaches, and malicious attacks requires implementing strong encryption, authentication mechanisms, and comprehensive security protocols.
- Power Consumption: IoT devices often operate on limited power sources, including batteries and energy harvesting. Optimizing power consumption and extending device lifespan are critical challenges that often require efficient power management techniques, low-power components, and energy-saving protocols.
- Reliability: In addition to the above challenges, ensuring reliable connectivity is a crucial aspect of IoT deployments. This is especially true for IoT devices designed to move around or inhabit changing environments. With IoT devices that constantly move, it’s essential to have a plan in place for dealing with connectivity failures.
Trends in IoT Connectivity
Technological advancements and shifting industry demands mean that the IoT connectivity landscape is constantly evolving. While it’s difficult to say precisely what the future holds, we can pinpoint several emerging trends shaping the future of IoT connectivity, including:
- LPWAN Growth: We’ve noticed significant growth in the deployment of LPWAN networks over the past few years. New protocols, such as LoRaWAN, are breathing new life into this sector.
- Cellular Improvements: Cellular communication is big business, and investors are eager to support innovation in this field.5G network roll-outs are offering new possibilities in data transfer speeds and lower latency. Power optimizations from cellular modem developers are making battery-powered cellular IoT devices more and more effective.
- Protocol Advances: IoT protocols are constantly evolving.LoRaWAN recently added repeater support to extend its range, for example, and Bluetooth’s Coded PHY is charting a path to longer-range Bluetooth connections. These exciting advancements promise to positively impact IoT functionality in the near future.
These trends are reshaping how IoT devices connect and communicate, opening doors to new applications and possibilities. Be sure to subscribe to our blog to stay up to speed on new IoT developments and industry trends.
IoT Connectivity in Action
IoT connectivity is akin to a master key, unlocking countless opportunities across various industries. It’s completely reshaping how businesses operate and opening doors to new revenue opportunities. Here are some key use cases that highlight the transformative impact of IoT connectivity:
PowerX
Very built a comprehensive solution for PowerX, enhancing their smart home monitoring suite by integrating LoRa networks. This robust connectivity framework became the cornerstone of PowerX’s ability to monitor water, electricity, and gas usage in real time. The hub, linking seamlessly with user networks via Wi-Fi or Ethernet, cast a long-range, low-power, and secure wireless signal. This foundational connectivity structure laid the groundwork for a user-friendly experience and empowered customers with valuable insights into their energy consumption.

To achieve this, we embarked on a Technical Design Sprint, auditing PowerX’s systems to identify and leverage opportunities for improvement. The focus shifted to LoRa technology, optimizing its integration into the hardware and software platforms. This process involved preparing the systems for scale, implementing firmware improvements, and restructuring the back-end infrastructure. The goal was to ensure that the connectivity between the hub and sensors was not only robust but also capable of delivering live and historical utility data to users.
From there, our attention turned to new feature development, honing in on the improved connectivity’s transformative impact. The LoRa-based hub seamlessly communicated with sensors, enabling users to set custom saving goals, manage entire home energy usage, and receive alerts on mechanical issues.
Tattlebox
Tattlebox wanted to enhance its security solution, foreseeing the need to transmit real-time updates for users concerned about the theft of mobile assets. To achieve this, Very adopted an Agile hardware development approach, swiftly integrating a vital cellular component into Tattlebox’s battery-powered system. The strategic addition of cellular connectivity enabled users to receive immediate security alerts, ensuring the safety of their belongings while on the move.
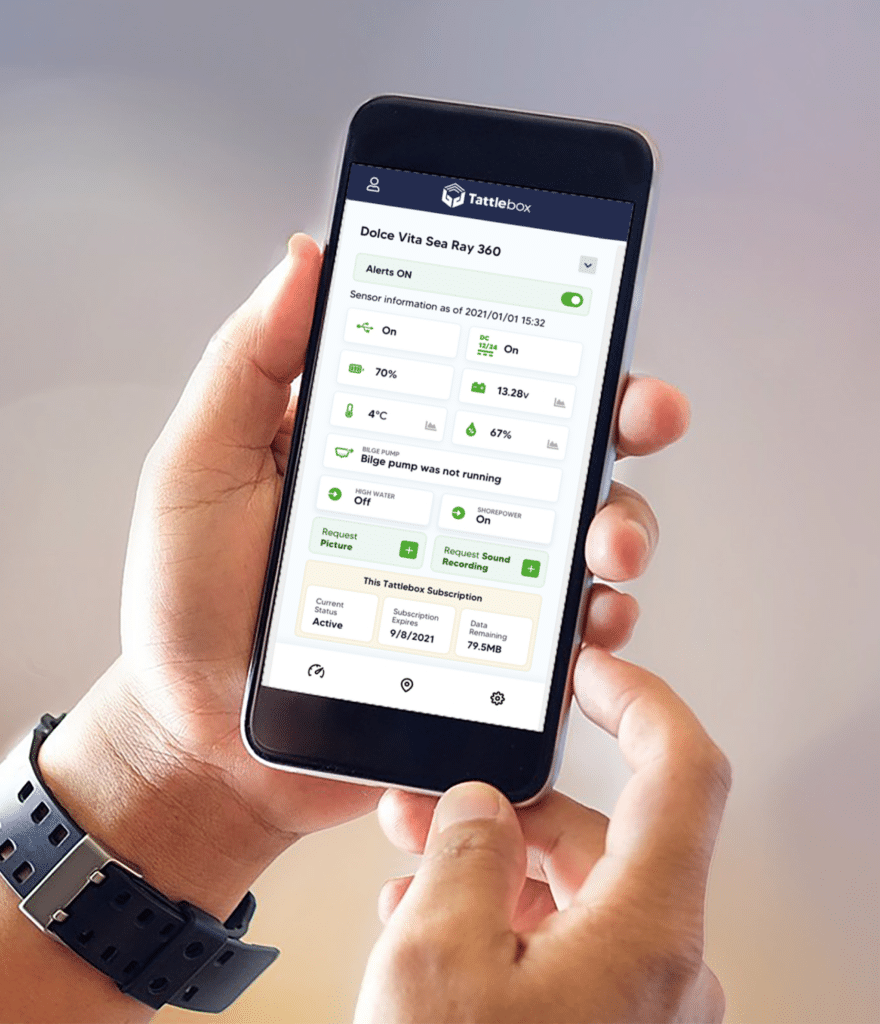
In this pursuit, the focus during the prototype-led development was on optimizing cellular connectivity for seamless communication. Our development encompassed crafting a custom printed circuit board assembly (PCBA) and enclosure, facilitating rapid testing and iteration. The primary objective was to guarantee that Tattlebox users could rely on timely updates and effective security reporting, leveraging the power of cellular connectivity.
Final Thoughts
Picture this: a retail space where the HVAC system anticipates and prevents potential issues before they arise, ensuring a consistently comfortable shopping environment. Now, imagine a manufacturing facility where smart HVAC technology regulates temperature and humidity, optimizing production conditions seamlessly. These may sound like dreams, but with the continuous advancements in IoT connectivity, many businesses are already turning these dreams into reality by leveraging innovation to enhance customer experiences and operational efficiency.
These use cases exemplify the diverse applications of IoT connectivity, showcasing its ability to drive efficiency, improve outcomes, and create value across industries. By embracing IoT connectivity, businesses can elevate their operational excellence and establish a competitive edge.