BLOG
How to Keep Your IoT Devices Secure Through Frequent System Updates
System updates are a bit like routine dentist visits: highly necessary but often postponed. However, when you finally check them off your to-do list, you’re glad you did. And more importantly, they can prevent underlying issues from becoming catastrophic—whether those may be holes in your teeth or in your cybersecurity approach.
If you plan to bring connected devices to market, don’t overlook frequent system updates as part of your IoT security and device management strategy. Dependencies like device drivers and operating systems are prone to attacks, and, as we’ll explore below, can be safeguarded against malicious players by regularly updating software components. Let’s dive in.
Recent and Real: Current Threats in the IoT Landscape
Connected devices attract malicious players—this is an unfortunate reality of the digital landscape. Higher volumes of connected endpoints translates to greater risk of vulnerabilities, some of which have emerged only in recent years. Here are a few examples.
- Ripple20: Ripple20 is a set of 19 vulnerabilities discovered in Treck, a small library that uses a TCP/IP stack. Companies use this library to enable devices or software to connect to the internet via TCP/IP connections. If exploited, these vulnerabilities could lead to unauthorized remote access, data theft, and even the complete takeover of devices such as smart home products, industrial tools, and medical equipment. Addressing these vulnerabilities requires patching the affected devices with updated software and firmware.
- Amnesia:33: This set of 33 vulnerabilities affects four widely-used open-source TCP/IP stacks (uIP, FNET, picoTCP, and Nut/Net). The risks include attacks such as remote code execution, service denial, and information leaks, impacting millions of IoT devices worldwide.
- Spectre and Meltdown: These hardware vulnerabilities were discovered in early 2018 and affect most modern processors. They allow attackers to steal sensitive information from a device’s memory by exploiting speculative execution. Firmware and operating system updates can help mitigate the risk associated with these vulnerabilities.
Though vulnerabilities are an inherent component of connected IoT ecosystems, undertaking frequent risk mitigation procedures can prevent attacks and ensure product integrity. That’s where system updates come into play.
Mitigating Security Risks With Frequent System Updates
Frequent system updates are the key to addressing vulnerabilities and ensuring IoT device security. By regularly updating software components like device drivers, operating systems, and libraries, businesses can seal potential attack vectors and keep devices secure. These updates can range from patching critical security vulnerabilities to mitigating performance and stability issues.
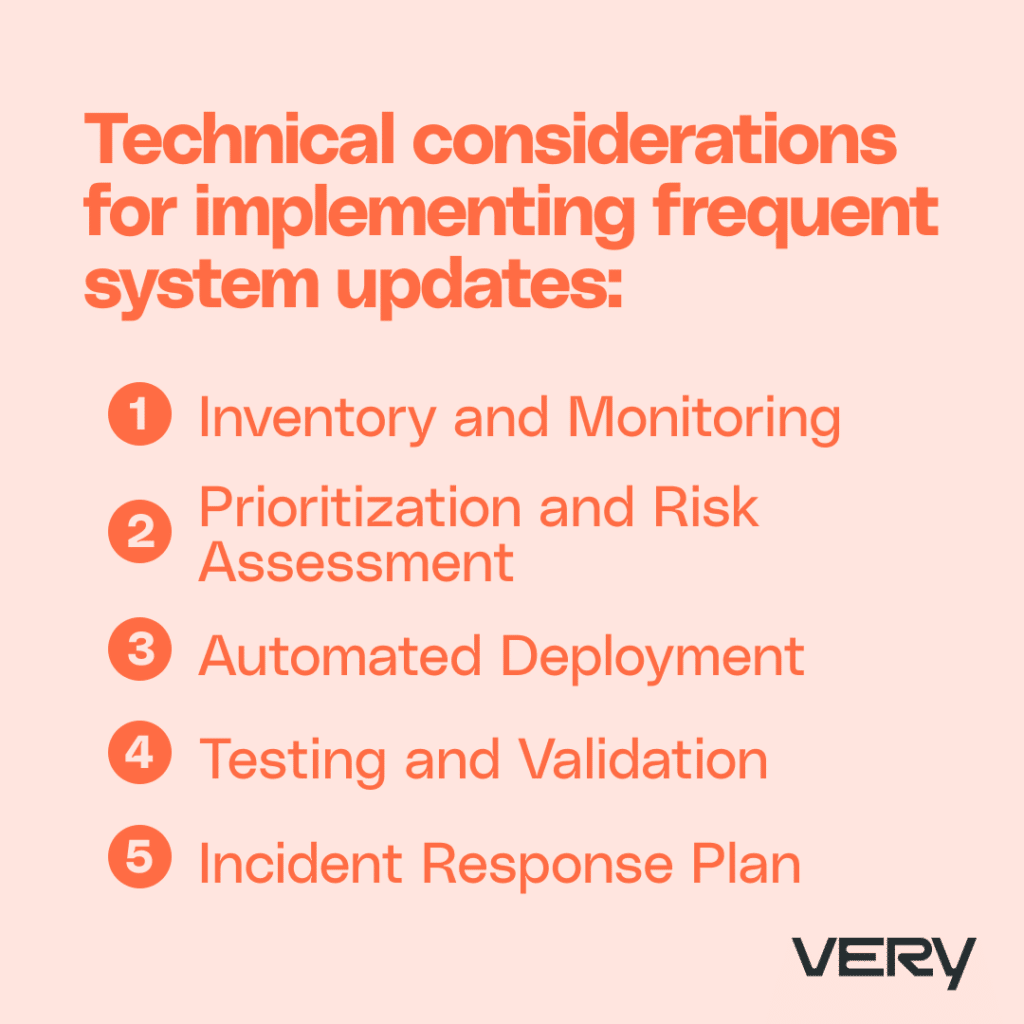
Below are a few technical considerations for implementing frequent system updates:
- Inventory and Monitoring: Maintain an accurate inventory of your IoT devices and their dependencies, including operating systems, device drivers, and libraries. Monitor for vulnerability disclosures, security advisories, and patch releases related to these components.
- Prioritization and Risk Assessment: Evaluate the severity of discovered vulnerabilities and prioritize updates based on the potential impact. Focus on high-risk vulnerabilities first and consider the complexity of the required updates.
- Automated Deployment: Automate the deployment of software updates to reduce the time and effort required to maintain device security. Utilize Over-the-Air (OTA) updates to deliver patches remotely and streamline the update process.
- Testing and Validation: Before deploying updates, test them thoroughly in a controlled environment to ensure compatibility and avoid unintended side effects. Validate the effectiveness of updates in addressing the targeted vulnerabilities.
- Incident Response Plan: Develop an incident response plan to deal with vulnerabilities that cannot be patched immediately. This plan should include strategies for containment, mitigation, and recovery.
Frequent system updates are, of course, only one piece of the puzzle that is IoT security. For a deeper dive into IoT security, you can read our recent whitepaper on this topic.
The Importance of IoT Security
Innovation in IoT involves a careful balancing of risks and rewards. At Very, we believe that the right IoT security and device management strategy can greatly decrease those risks, empowering businesses to spearhead their boldest IoT projects with peace of mind.